Getting to the Nucleus of the Matter.
We use our non-viral s50 capsule technology platform and structural insights
to provide partners with innovative and disruptive solutions
for next-generation gene therapy delivery.
We use our non-viral s50 capsule technology platform and structural insights to provide partners with innovative and disruptive solutions for next-generation gene therapy delivery.

Our Story
Surtovol™ is a pioneer in
ligand-directed nanocapsule delivery of gene therapy at the biologically-relevant sub-50 nanometer (“s50”) threshold.

Our Focus
We prioritize partnering in
next-generation gene therapy that restores protein and cell function — applications that are ideally-suited for s50 capsule’s non-inflammatory, non-immunogenic and large-payload profile.

Our Platform
At ~ 20 nm diameter, s50 capsules are 1/3rd size of liposomes, and co-opt size-sensitive lipid raft uptake into target cells.(1)
s50’s are also uniquely modular — RNA/DNA/pDNA cargo up to 17 kb, + any hydrophilic ligand (e.g., 1MM Da hyaluronan), can be used.
Reaching the nucleus
on the path less traveled.
s50 technology is a novel strategy for partners to overcome gene therapy’s #1 rate-limiting step — i.e., avoiding endolysosomal capture after entering the cell.
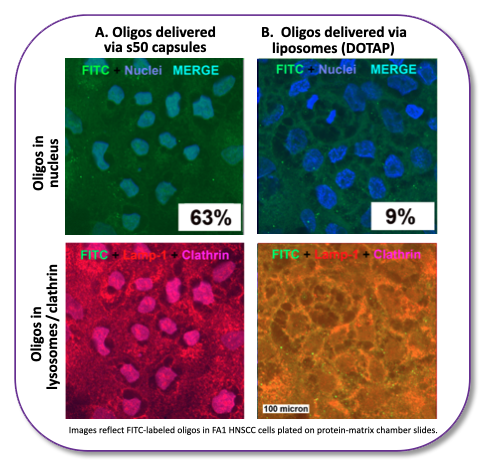
A. Employing biologically-relevant protein matrix chamber slides, s50 capsules co-opt the size-sensitive lipid raft pathway of cells and deliver the majority of their oligo cargo (shown here = 63%) to the nucleus.
B. By comparison, liposomes deliver a fractional share of their oligo cargo (shown here = 9%) to the nucleus.
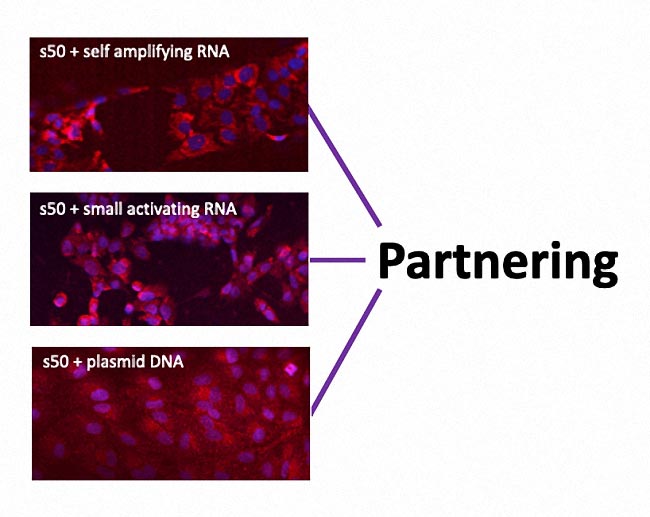
s50 in vivo: Overcoming a series of delivery barriers to effect a gene therapy cure.
The benefit of nucleus access is of course dependent upon the delivery vehicle’s ability to also overcome in vivo’s other delivery barriers.
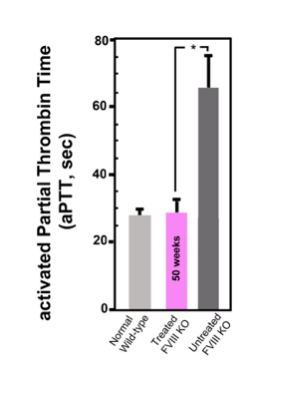
In this 50-week study(2) of hemophilia A mice treated IV with s50 capsules bearing a collaborator’s 12.8 kb pDNA, liver sinusoidal endothelial cells were targeted using 1MM Da hyaluronan ligands. No immune-suppression steps were used in this study.
Findings showed treatment resulted in an effective cure of hemophilia A in the subject mice, without any observed adverse effects.